COVID-19John Jacobs, 14 juni 2020Lost at familiar property |
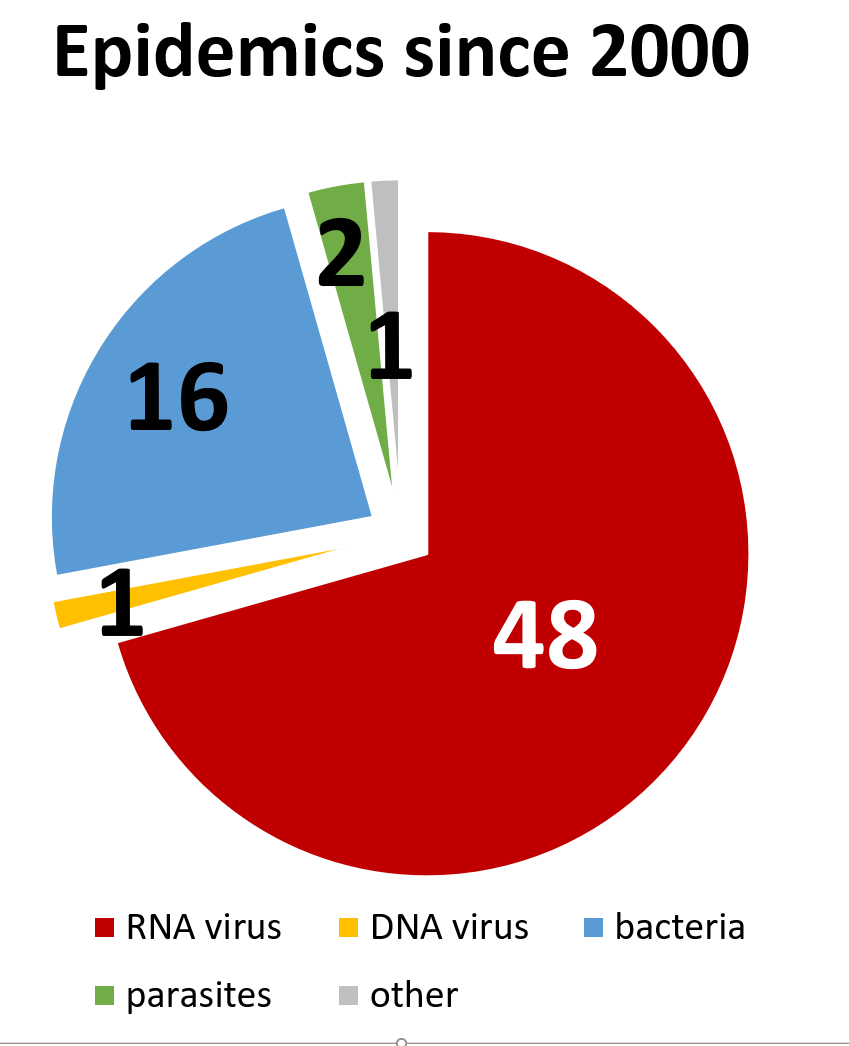
Figure 1. Epidemic since 2000
1. Predicted epidemic
COVID-19 is the 68th epidemic [1] in the last two decennia, 48 were caused by RNA viruses (Figure 1), and 3 by coronaviruses – including SARS and MERS. Vets have been familiar with even more epidemics at different species of pet and farm animals. Vets [2] and Asian doctors are experienced in the battle against epidemics like COVID-19.
Thus, although the people and most governments were surprised by the COVID-19 epidemic, virologist predicted this epidemic.[3] Three months ago all that was needed was to enter the numbers from partial data in the literature [4] and standard algorithms could do the calculations.[5] Scientist are transparent on their assumptions and methodology, to share their knowledge and logic with others and allow correction upon progressive insight.[6]
---
[1] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_epidemics
[2] https://hartblik.weebly.com/betere-bestrijding-van-de-epidemie.html
[3] https://hartblik.weebly.com/ontsnappende-virussen.html
[4] https://hartblik.weebly.com/versimpeld-model-corona-nl.html
[5] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mathematical_modelling_of_infectious_disease
[6] https://hartblik.weebly.com/addendum-correctie.html
Thus, although the people and most governments were surprised by the COVID-19 epidemic, virologist predicted this epidemic.[3] Three months ago all that was needed was to enter the numbers from partial data in the literature [4] and standard algorithms could do the calculations.[5] Scientist are transparent on their assumptions and methodology, to share their knowledge and logic with others and allow correction upon progressive insight.[6]
---
[1] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_epidemics
[2] https://hartblik.weebly.com/betere-bestrijding-van-de-epidemie.html
[3] https://hartblik.weebly.com/ontsnappende-virussen.html
[4] https://hartblik.weebly.com/versimpeld-model-corona-nl.html
[5] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mathematical_modelling_of_infectious_disease
[6] https://hartblik.weebly.com/addendum-correctie.html
2. Annoying virus
SARS-2 is not extremely lethal like MERS and Ebola but has a mortality rate between 0,6 and 2,9%.[1] A disease killing 1 to 2% of the patients should be taken seriously, and should not be allowed to infect more people to aim for herd immunity,[2] since this would cause hundreds of thousands victims in countries like the Netherlands.[3] Moreover, survivors, including those that were not hospitalized, suffer from major morbidities, even after months.[4]
Patients with SARS-2 do not pass away due to the virus, but due to their immune response against the virus. Inappropriate immune responses aggravate the disease with putative lethal consequences. It might be that the virus is disseminated through the body by antibodies, which may also cause infection of leukocytes. [5]
The virus immune pathology hampers the development of therapies and vaccines. The European organisation that approves medicines (EMEA) said that it will evaluate putative vaccines for their effectivity against infections, not for induced antibody titers. History teaches that to develop vaccines against an immune pathology is hard – 37 years was not enough for an anti-HIV vaccine.
---
[1] https://hartblik.weebly.com/beter-a-impact-covid-19.html
[2] https://hartblik.weebly.com/rekenen-zonder-getallen-7.html
[3] Netherlands 173.000 to 345.000. Belgium 115.000 - 229.000
[4] https://www.ad.nl/binnenland/longfonds-gezondheid-thuiszittende-coronapatienten-schrikbarend-slecht~a45346fe/
[5] https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0306987720311270?dgcid=author
Patients with SARS-2 do not pass away due to the virus, but due to their immune response against the virus. Inappropriate immune responses aggravate the disease with putative lethal consequences. It might be that the virus is disseminated through the body by antibodies, which may also cause infection of leukocytes. [5]
The virus immune pathology hampers the development of therapies and vaccines. The European organisation that approves medicines (EMEA) said that it will evaluate putative vaccines for their effectivity against infections, not for induced antibody titers. History teaches that to develop vaccines against an immune pathology is hard – 37 years was not enough for an anti-HIV vaccine.
---
[1] https://hartblik.weebly.com/beter-a-impact-covid-19.html
[2] https://hartblik.weebly.com/rekenen-zonder-getallen-7.html
[3] Netherlands 173.000 to 345.000. Belgium 115.000 - 229.000
[4] https://www.ad.nl/binnenland/longfonds-gezondheid-thuiszittende-coronapatienten-schrikbarend-slecht~a45346fe/
[5] https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0306987720311270?dgcid=author
3. Health and early intervention
Efficient treatment in early stage of disease will give the most health gain.[1] Preventing serious COVID-19 avoids the serious morbidity and reduces mortality. From a commercial point of view, this may not be the most interesting developments, since authorized but unpatentable drugs may be suitable for this, whereas commercial pharmacy drives on patents. Patients might be most interested in using authorized safe medication like vitamin D, Low dose interleukine-2, hydroxychloroquine. These interventions should be tested for efficacy and specific safety in COVID-19 patients. This could be a task for the government and UMCs. Early intervention could reduce SARS-2 to the level of a mild influenza. Some options:
[1] https://hartblik.weebly.com/bestrijding-covid19.html
[2] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmid/23840373/
[3] https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3585561
[4] https://hartblik.weebly.com/foute-afweer.html
[5] https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(20)31180-6/fulltext
[6] https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00262-004-0641-6
[7] https://journals.prous.com/journals/servlet/xmlxsl/pk_journals.xml_summaryn_pr?p_JournalId=4&p_RefId=1025703
[8] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20044643
- The daily recommended amount of vitamin D has been shown effective against respiratory RNA viruses.[2] Patients with vitamin D deficiency are at risk for lethal COVID-19.[3] It is considered likely that normal doses of vitamin D could be effective for COVID-19 patients. [4]
- There is much scientific commotion on hydroxychloroquine with macrolide (azithromycin)[5] and zinc in early COVID-19. Hydroxychloroquine is safe for long-term treatment of malaria and rheumatic disease – treatment of COVID-19 would be short term in an early stage. Efficacy against COVID-19 needs be shown.
- Interleukine-2 (IL-2) has been used since the 1980s to stimulate the immune system. At first only in high doses with huge toxicity, but low doses have been shown more effective. [6] Reducing doses by a factor 100 to 1000 avoids toxicity. Low dose IL-2 stimulates the immune system and effectivity has been shown against virus infection by HIV[7], HBV and HCV.[8] Efficacy against COVID-19 needs be shown.
[1] https://hartblik.weebly.com/bestrijding-covid19.html
[2] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmid/23840373/
[3] https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3585561
[4] https://hartblik.weebly.com/foute-afweer.html
[5] https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(20)31180-6/fulltext
[6] https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00262-004-0641-6
[7] https://journals.prous.com/journals/servlet/xmlxsl/pk_journals.xml_summaryn_pr?p_JournalId=4&p_RefId=1025703
[8] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20044643
4. Known strategy
Virologists know how viruses spread, and this is remarkably different from bacteria.[1] Non-virologists[2] often confuse this, and think in bacterial models with intermediary sources or multiplications.[3] Viruses can only reproduce in the host, and their activity decreases outside of the host.
Respiratory viruses, like SARS-2 are spread through the air,[4] which is epidemiologically confirmed.[5] Being near an infected person and breathing the aerosol could lead to an infection. The risk is modulated by the amount of virus production, the deepness of breathing, the distance between both persons and the time of being in close proximity. Sneezing could transport virus-containing aerosol over a distance of 10 meters. A simple cotton facemask inhibits the free air flow. [6] This is the rationale behind sneezing in the elbow. Facemasks cover a larger relevant area than the elbow. Non-medical facemasks offer limited protection to the wearer, since the virus could diffuse through the pores.
---
[1] https://hartblik.weebly.com/bestrijding-covid19.html
[2] https://hartblik.weebly.com/expert-opinion.html
[3] In general, bacteria spread through an intermediate source, like surfaces (pseudomonas), meat (salmonella), milk (listeria), water sources (Cholera) or water recycling systems (legionella). Temperature and bacterial growth conditions are crucial for the intermediate source and its potential to infect.
In virology, spreading is, generally, directly from human to human.
[4] https://www.thelancet.com/action/showPdf?pii=S0140-6736%2820%2930918-1
[5] https://www.pnas.org/content/early/2020/06/10/2009637117
[6] https://hartblik.weebly.com/mondkapjes.html
Respiratory viruses, like SARS-2 are spread through the air,[4] which is epidemiologically confirmed.[5] Being near an infected person and breathing the aerosol could lead to an infection. The risk is modulated by the amount of virus production, the deepness of breathing, the distance between both persons and the time of being in close proximity. Sneezing could transport virus-containing aerosol over a distance of 10 meters. A simple cotton facemask inhibits the free air flow. [6] This is the rationale behind sneezing in the elbow. Facemasks cover a larger relevant area than the elbow. Non-medical facemasks offer limited protection to the wearer, since the virus could diffuse through the pores.
---
[1] https://hartblik.weebly.com/bestrijding-covid19.html
[2] https://hartblik.weebly.com/expert-opinion.html
[3] In general, bacteria spread through an intermediate source, like surfaces (pseudomonas), meat (salmonella), milk (listeria), water sources (Cholera) or water recycling systems (legionella). Temperature and bacterial growth conditions are crucial for the intermediate source and its potential to infect.
In virology, spreading is, generally, directly from human to human.
[4] https://www.thelancet.com/action/showPdf?pii=S0140-6736%2820%2930918-1
[5] https://www.pnas.org/content/early/2020/06/10/2009637117
[6] https://hartblik.weebly.com/mondkapjes.html
5. Hidden epidemic
Analysis from an isolate cruise ship showed that 81% of the infections were asymptomatic and 0,8% lethal.[1] Numbers could vary in different populations that are more of even less sensitive for the virus. In SARS-2, like most viruses, most infected persons shed virus prior to becoming ill. This is crucial for viruses, since diseased people and animals will withdraw themselves from society and avoid contacts with other, which would avoid infections. Asymptomatic and presymptomatic people can infect other people unknowingly.
Hidden infections can be uncovered by testing. Testing everybody is virtually impossible and causes many false positives. Thus, virologist investigate the source of infection and the contacts of the infected person. When new infected persons are found, this procedure is repeated. All infected persons should remain quarantined until they are free of the virus.
This proactive testing requires an excellent organization for testing, tracing and logistics. East-Asian countries were well prepared (section 7), countries like Germany only partially, and Belgium and the Netherlands not well at all.
---
[1] https://thorax.bmj.com/content/thoraxjnl/early/2020/06/09/thoraxjnl-2020-215091.full.pdf
Hidden infections can be uncovered by testing. Testing everybody is virtually impossible and causes many false positives. Thus, virologist investigate the source of infection and the contacts of the infected person. When new infected persons are found, this procedure is repeated. All infected persons should remain quarantined until they are free of the virus.
This proactive testing requires an excellent organization for testing, tracing and logistics. East-Asian countries were well prepared (section 7), countries like Germany only partially, and Belgium and the Netherlands not well at all.
---
[1] https://thorax.bmj.com/content/thoraxjnl/early/2020/06/09/thoraxjnl-2020-215091.full.pdf
6. Isolate cases or lockdown
Virologists advise to stop an epidemic by isolating infected people. In case of (temporary) incompetence to do so, the lockdown might be an alternative. A lockdown could be effective if everyone participates. It should be noted that a lockdown has major impact on social contacts and economy. It is not a suitable strategy for long-term disease control.
Virologist advise testing, proactive testing and isolation of infected persons. This is, unlike the lockdown, only a temporary isolation, the disease period plus two weeks. This has limited impact on society and economy, since > 99% of the populations has normal freedom.
Virologist advise testing, proactive testing and isolation of infected persons. This is, unlike the lockdown, only a temporary isolation, the disease period plus two weeks. This has limited impact on society and economy, since > 99% of the populations has normal freedom.
7. Evaluation of current approach
How do countries fight the epidemic so far? The Corona Dashboard[1] shows countries with nearly 10, 100 and 1000 fatalities per million. Correction for underreporting and age is limited to a factor 2 and not 10 of 100. Similar for climate, population density, communities, culture and other factors that could influence the spread of the epidemic. Using this factor 10, allows the discrimination of four groups:
---
[1] https://hartblik.weebly.com/corona-dashboard.html & https://gijsvanloef.nl/
[2] Taiwan is an island near China’s mainland and has a mortality rate of 0,3 per million. Taiwan understood the Chinese messages and reacted early and precise.
[3] https://hartblik.weebly.com/cijfers-en-data.html
[4] https://stories.lab.nos.nl/artikel/396/waarom-nederland-niet-in-lockdown-gaat
- 10 mortalities per million are found in some East-Asian and Australian countries. Alerted by the SARS-1 epidemic in 2002, Taiwan,[2] Japan, Australia, New-Zealand and Zuid-Korea started proactive testing immediately.
- 100 mortalities per million are found in Germany, Austria and the Scandinavian countries (except Sweden) that focussed at proactive testing but were less disciplined that the former group.
- 1,000 mortalities per million are found in Italy and Spain that were overwhelmed by the epidemic. These numbers are also found in the United Kingdom, Belgium and Sweden that only performed very limited forms of proactive testing. Occasionally, the philosophy was only to inhibit the epidemic with a partial lockdown.
- 10,000 mortalities per million are the expected numbers of an uncontrolled epidemic. Infection rates of about 6 – 7% in the previous group shows that the number of lethal victims could be easily ten times as high. This is the number to take for calculations how many lives are saved due to the lock down.
---
[1] https://hartblik.weebly.com/corona-dashboard.html & https://gijsvanloef.nl/
[2] Taiwan is an island near China’s mainland and has a mortality rate of 0,3 per million. Taiwan understood the Chinese messages and reacted early and precise.
[3] https://hartblik.weebly.com/cijfers-en-data.html
[4] https://stories.lab.nos.nl/artikel/396/waarom-nederland-niet-in-lockdown-gaat
8. Improve the fight
Jaap van Dissel, bacteriologist and chief infection disease control of the RIVM, states correctly that the epidemic is far from over and could last for a few more years. Last week he still thinks of building herd immunity, one of the goals aim of the national vaccination program, but in this case without a vaccine (see section 2). The mathematical model contains cycli of turning the lockdown on and off.[1] Simple extrapolations show that this could cause hundreds of thousands of lives (see part 2). We do not think that would be morally acceptable.
Veterinary virologists always want to completely stop an epidemic – primarily for economic reasons.[2] East-Asia and Australia showed that this standard anti-epidemic approach is suitable for COVID-19. The epidemic spreads more rapid, now countries are relaxing the lockdown.[3] This is the moment to think about long-term antiviral strategy.
---
[1] https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2020.00262/full
[2] https://hartblik.weebly.com/betere-bestrijding-van-de-epidemie.html
[3] https://www.nrc.nl/nieuws/2020/06/12/geeft-de-wereld-de-strijd-al-op-a4002658
Veterinary virologists always want to completely stop an epidemic – primarily for economic reasons.[2] East-Asia and Australia showed that this standard anti-epidemic approach is suitable for COVID-19. The epidemic spreads more rapid, now countries are relaxing the lockdown.[3] This is the moment to think about long-term antiviral strategy.
---
[1] https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2020.00262/full
[2] https://hartblik.weebly.com/betere-bestrijding-van-de-epidemie.html
[3] https://www.nrc.nl/nieuws/2020/06/12/geeft-de-wereld-de-strijd-al-op-a4002658
Figure 2. Jaap van Dissel. Bacteriologist and director of the infectious disease control center of the RIVM, the Netherlands
9. Recommendations
- The basis is full proactive testing (see section 4). [1] This is a required to end the lockdown.
- Protect as many people as possible, especially caretakers with medical facemask. Use normal facemasks when medical are unavailable and people are in close proximity for prolonged periods.
- Improve the intervention of early COVID-19 and natural immunity (see section 3) Invest in research for intervention in early cases that reduce the number of severe COVID-19.
- Stop large events until people are sufficiently protected against COVID-19,[2] i.e. it becomes not more dangerous than the flu. Therapy in early stages might be more successful than vaccination.
[1] https://hartblik.weebly.com/bestrijding-covid19.html
[2] https://hartblik.weebly.com/verloren-door-te-weinig-kennis.html
John Jacobs, 14 juni 2020
In samenwerking met Platform Betrouwbare Zorgcijfers
In samenwerking met Platform Betrouwbare Zorgcijfers